Calibration
Calibration involves setting or correcting an instrument by comparing its output to a standard or known measurement. It is essential for ensuring that an instrument provides accurate readings over time. Calibration typically involves a series of adjustments to align the instrument with the standard.
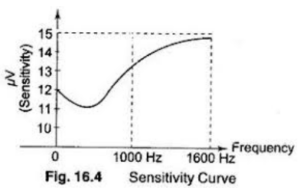
Hysteresis
Hysteresis refers to the phenomenon where the output of an instrument depends not only on its current input but also on its history of past inputs. This is commonly observed in materials and sensors where the response to increasing input differs from the response to decreasing input.
- Hysteresis Curve: A graph typically showing the input-output relationship during both increasing and decreasing inputs. I will create an image illustrate a typical hysteresis curve
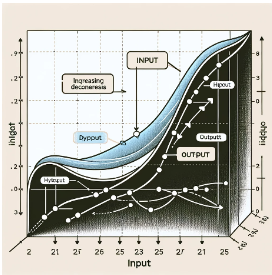
Turndown
Turndown ratio, also referred to as Rangeability, is the ratio of the maximum flow rate to the minimum flow rate an instrument can measure with acceptable accuracy. It indicates the operational flexibility of devices like flow meters.
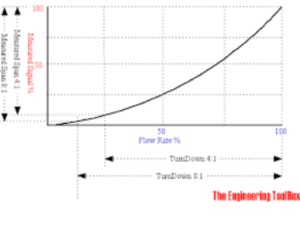
Sensitivity
It describes the responsiveness of an instrument to changes in the measured quantity. It indicates how much the output of an instrument changes when the input quantity changes. In other words, sensitivity is the ratio of the change in the output signal to the change in the input signal.